The majority of engineers are aware of the best practices and norms related to DNS setup. Private DNS, an alternate method of handling the records needed to resolve internal resource addresses by keeping those files private (not able to be resolved by public DNS), offers several advantages that not everyone is aware of. Private-DNS is particularly attractive for both basic and complicated topologies due to its excellent security features, wide range of customizations, and more freedom in using the organization’s DNS records. Therefore, understanding what is private DNS may help you successfully configure it on your laptop or mobile devices.
Human-friendly domain names are converted to computer-friendly IP addresses using DNS. Your device’s DNS requests are encryption before it sends them to a DNS server using private DNS. It can increase your online privacy when paired with a third-party DNS provider that protects your privacy. Private DNS, in contrast, is not necessary while utilizing a VPN and may even compromise the security of your connection.
Keep reading and exploring to learn what does private DNS mean and how to change the DNS on iPhone, Android phone, and laptop.

Table of Contents
What is Private DNS Mode?
Private DNS is a way to generate a custom DNS namespace within an internal network. Without using public DNS servers, it enables businesses to create their own domain names that are resolvable by the devices on their internal networks.
DNS requests frequently arrive in unreadable plaintext, in contrast to the majority of connections to websites, which are safe via HTTPS. This implies that even if a third party resolves the DNS requests, anyone with access to them—like your ISP—can read them.
An ISP could easily monitor and report the DNS requests to third-party resolvers if it wanted to spy on its users more (as it could be obliged to do by a more stringent government). By screening these requests, it may even impose censorship using more advanced technology.
By encrypting your DNS requests as they move between your mobile device and a third-party DNS server, private DNS stops this. This guarantees that your DNS requests won’t be seen by your ISP or anybody else keeping an eye on your internet connection. That is why you must know what is private DNS in 2025.
Therefore, in comparison to conventional unencrypted DNS queries, private DNS offers a notable improvement in DNS privacy and security. But it also has a number of drawbacks, which we’ll talk about later.
How Private DNS Works?
Creating a unique DNS namespace inside an internal network is possible with it. Without using public DNS servers, it enables businesses to create their own domain names that are resolvable by the devices on their internal networks.
This is how private DNS functions
- Within its private network, the company installs a private DNS server. For the company’s unique domain names, this DNS server serves as the authoritative DNS server.
- Custom domain names are made by the company and linked to the IP addresses of its equipment.
- Zone files on the private DNS server include information about IP addresses and custom domain names.
- A device on the private network contacts the private server to reach another device using its unique domain name.
- It deliver the IP address to the device making the request after searching its zone files for the IP address linked to the domain name.
- The requesting device can then connect to the appropriate device on the private network using the IP address.
Protocols For Private DNS

One of the three security protocols—DNS-over-TLS (DoT), DNS-over-HTTPS (DoH), or DNSCrypt—is used to accomplish private DNS. Here are the main protocols of what is Private DNS on Android:
DNS over TLS
To make sure the data cannot be readily intercepted or changed, DoT encrypts DNS requests using the Transport Layer Security (TLS) protocol. Because DoT traffic doesn’t mix in with other kinds of communication, networks can more easily restrict or monitor it because it operates on port 853.
Because of this, DoT is the recommended option for networks that want some degree of control over the traffic that flows through them. Compared to DoH, DoT is also easier to deploy at the server level.
Also Read: How To Fix DNS Server Not Responding: Step by Step Guide To Fix
DNS over HTTPS
DoH encrypts DNS requests using HTTPS, the technology that protects all private data on the internet. DoH encrypts DNS queries using TLS, similar to DoT; however, DoH connections are routed on port 443, which means they are mixed in with normal HTTPS web traffic. Because of this, DoH is more private and resistant to censorship than DoT, as it is harder for observers to discern DNS traffic from other kinds of online traffic.
DNSCrypt
Though it has certain extra characteristics that make it better than DoH, DNSCrypt, the oldest private DNS system, is quite comparable to DoH. However, DNSCrypt necessitates the use of third-party software because it is not commonly supported through operating systems and web browsers.
DNS Over QUIC
The QUIC transport protocol, which is similarly intended for low-latency and secure internet connections, is used by DNS over QUIC (DoQ) to encrypt DNS requests. DoQ is perfect for mobile and high-speed networks because it decreases latency and connection setup times by transmitting DNS requests via QUIC. Additionally, the protocol provides resilience against congestion and packet loss, guaranteeing a quicker and more seamless surfing experience even in the face of difficult network circumstances. Let’s now discuss how you can configure private DNS in our What is Private DNS on my phone guide.
How to Configure Private DNS on Every Device? Step-by-Step Guide

Here is a step-by-step guide from which you can easily configure private DNS on your device:
How To Change The DNS On Android?
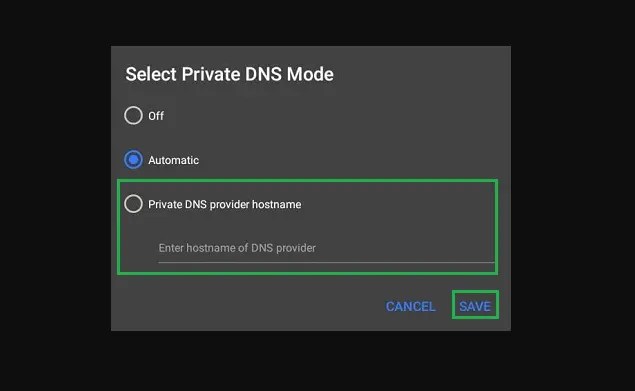
By accessing the device’s settings and choosing the network and internet choices, Android users may quickly enable Private DNS. Click Save after selecting Private DNS and entering the hostname of the Private DNS provider, such as 1dot1dot1dot1.cloudflare-dns.com.
For Android users, Cloudflare’s blog also provides a thorough guide on how to utilize the private DNS function.
Also Read: DNS Load Balancing: How It Works and Why It Matters
How To Change The DNS On Windows?
On a Windows device, private DNS setup is rather simple. To find “Network and Sharing Center,” press the Windows Key.
After that, choose “Change adapter settings.” Next, choose “Properties,” and then “Internet Protocol Version 4.”
Lastly, pick “Properties” once more, pick “Use the Following DNS Server Addresses,” and enter your private DNS provider’s networking IP addresses.
How To Change the DNS on iPhone?

iPhone private DNS configuration is a little different from Android and Windows setups. First, select Wi-Fi from the Settings menu, then click the “i” symbol next to your network connection. After clicking “Configure DNS,” choose “Manual.” To add the IP address of the private DNS provider, you should now see an option labeled “Add Server.”
How To Change The DNS On Mac?

There are a few simple steps involved in setting up private DNS on an Apple Mac. First, search for “System Preferences” using Spotlight, then choose Network. Click the Advanced button from here. To add the hostname or the IP address of your private DNS provider, click the “+” button on the DNS tab.
Private DNS Best Practices And Implementation

The following steps can maximize the possibility for successful use of private DNS and aid in its deployment in learning what is Private DNS.
Make a Thorough Plan
The following factors you must take into account while planning a DNS rollout.
DNS should operate on a domain controller (DC) in a Windows server environment. Many businesses decide to set up at least one physical server and an arbitrary number of virtual servers for redundancy, and DCs are typically installed in pairs.
The most important aspect of the planning process will be the software that is selected. In principle, Windows’ standard DNS capabilities are the simplest to set up and reduce the possibility of configuration errors. Windows Active Directory and Windows DNS have integrations.
The most important aspect of the planning process is the software that has selection. In principle, Windows’ standard DNS capabilities are the simplest to set up and reduce the possibility of configuration errors. By integrating with Windows Active Directory, Windows DNS builds a database of network services.
Select The Appropriate Architecture
There are many different use cases for each of the DNS architectures previously discussed; therefore, it’s critical to consider your company as a whole and assess your needs.
Generally speaking, the architecture used should support expansion of both clients and locations. Assume, for instance, that a company now has 100–200 clients and operates from a single physical location, but it hosts the majority of its apps internally. Split horizon DNS would be a great option in this case, as it offers the flexibility to use both the public and international domain names to resolve to various places based on the client’s location. This is one of the main DNS best practices you must remember to know what is private DNS in 2025.
Test Thoroughly
To make sure the private DNS implementation is operating properly and offering the required degree of performance and dependability, extensive testing is necessary. Examine every facet of the DNS resolution procedure, such as error handling, caching, and name resolution.
As a test group, begin setting up a small workstations to utilize the new DNS servers as the main DNS. DNS resolution may be examined from the workstations using a variety of tools, such as:
- On Windows devices, nslookup
- Test for DNS Leaks
- MX Toolbox DNS Verification
- Keep an eye on and maintain
After the private DNS deployment is operational, it’s critical to do routine system monitoring to identify and resolve any potential problems.
Conclusion
Improved security, privacy, and performance are just a few advantages that private DNS may provide businesses and networks. Organizations can enhance network security and dependability by gaining greater control over the DNS resolution process through the use of a dedicated DNS server or other private DNS architecture. Comment below if you have any queries about what is Private DNS on my phone. Our team will assist you accordingly.
FAQs (Frequently Asked Questions)
Why Do People Use Private DNS?
Private DNS is mostly used to increase internet security and privacy, while it may help speed up networks.
What Happens If DNS Is Off?
Accessing websites using their domain names (like temok.com) will become impossible if the DNS (Domain Name System) is off or malfunctioning.
What Does It Mean When Your Phone Says Private DNS Server Cannot Be Accessed?
“Private DNS server cannot be accessed,” which appears on your phone, usually indicates that your device is experiencing issues connecting to the private DNS server that you have set up.
What Does Private DNS Mean On A Cell Phone?
You may encrypt your DNS queries using private DNS on your phone. It prevents your ISP and other third parties from seeing the websites you visit.
